最近项目中一处定时任务出现了问题:定时任务没有按照原先预想的周期执行。问题是因为对 ThreadPoolTaskScheduler 中定时任务处理类的原理不熟悉导致的,下面就结合问题看下 ThreadPoolTaskScheduler 中的三个定时任务处理方法。
schedule()
原代码如下:
1
| ScheduledFuture future = threadPoolTaskScheduler.schedule(timerCollectData, new CronTrigger("*/18 * * * * ?"));
|
这段代码使用 ThreadPoolTaskScheduler 中的 schedule() 结合 cron 表达式来实现定时任务,预想的是每隔 18s 执行一次,但是实际测试发现执行周期并不稳定,测试代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| @org.junit.Test
public void fun1() throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler scheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
scheduler.setPoolSize(10);
scheduler.initialize();
scheduleWithCron(scheduler, 1, 18L, 0L);
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
private void scheduleWithCron(ThreadPoolTaskScheduler scheduler, int currentTaskNo, long intervalSecond, long sleepSecond) {
scheduler.schedule(() -> {
System.out.println("==========================================任务" + currentTaskNo + "的定时任务触发,当前时间:" + DateUtils.DateFormatByStr(new Date()));
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepSecond * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("任务" + currentTaskNo + "执行,当前时间:" + DateUtils.DateFormatByStr(new Date()));
}, new CronTrigger("*/"+ intervalSecond +" * * * * ?"));
}
|
测试结果如下:
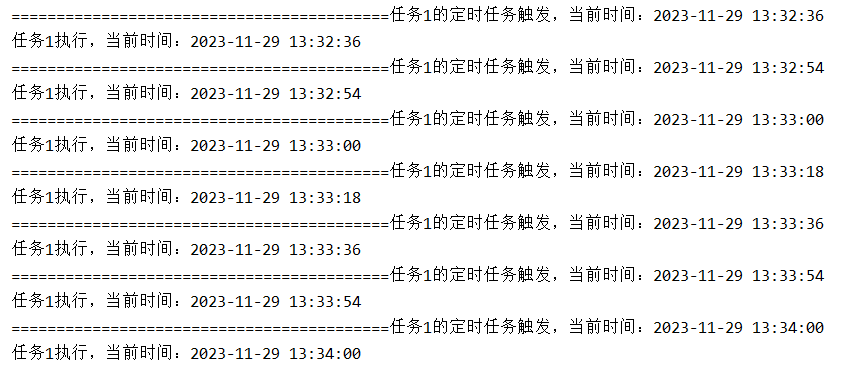
查阅了相关文档,找到了问题的原因。cron 表达式中,秒级任务是以一分钟为范围来执行的,比如上面定义的 */18 * * * * ?,意思就是任务会在每分钟的 0s、18s、36s、54s 执行,在 54s 执行后,6s 后进入下一分钟的 0s,又会触发任务执行。而如果定义的表达式中秒数恰好是 60 的约数,那么就不会有问题,而上面定义的 18s 并不是 60 的约数,因此定时任务的周期不会按照预想的结果执行。
scheduleAtFixedRate() 和 scheduleWithFixedDelay()
在 ThreadPoolTaskScheduler 中还提供另外的方法来实现定时任务的触发:scheduleAtFixedRate() 和 scheduleWithFixedDelay()。
这里直接放上 StackOverflow 上关于这两个方法区别的讨论:地址

但是有一个问题,如果上面煮咖啡的时间超过了一小时,那定时任务会如何触发呢?写一个 Demo 来测试一下,定时任务间隔设置为 3s,任务执行时间设置为 5s:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| @org.junit.Test
public void fun1() throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolTaskScheduler scheduler = new ThreadPoolTaskScheduler();
scheduler.setPoolSize(10);
scheduler.initialize();
scheduleAtFixedRate(scheduler, 1, 3L, 5L);
Thread.currentThread().join();
}
private void scheduleWithFixedDelay(ThreadPoolTaskScheduler scheduler, int currentTaskNo, long intervalSecond, long sleepSecond) {
scheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
System.out.println("==========================================任务" + currentTaskNo + "的定时任务触发,当前时间:" + DateUtils.DateFormatByStr(new Date()));
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepSecond * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("任务" + currentTaskNo + "执行,当前时间:" + DateUtils.DateFormatByStr(new Date()));
}, intervalSecond * 1000);
}
private void scheduleAtFixedRate(ThreadPoolTaskScheduler scheduler, int currentTaskNo, long intervalSecond, long sleepSecond) {
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
System.out.println("==========================================任务" + currentTaskNo + "的定时任务触发,当前时间:" + DateUtils.DateFormatByStr(new Date()));
try {
Thread.sleep(sleepSecond * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("任务" + currentTaskNo + "执行,当前时间:" + DateUtils.DateFormatByStr(new Date()));
}, intervalSecond * 1000);
}
|
先来看下 scheduleAtFixedRate() 的测试结果:

再看下 scheduleWithFixedDelay() 的测试结果:

两个方法都是等任务执行完毕,才继续执行下一个任务,其中 scheduleAtFixedRate() 会在上一个任务结束后,立刻开始执行下一个任务,scheduleWithFixedDelay() 则是在上一个任务结束后的 3s 后才开始执行下一个任务。



