JPA 全称 Java Persistence API,它是一套规范,常见的 JPA 实现包括:Hibernate、Spring Data JPA,目前一般使用 Spring Data JPA 框架。JPA 直接提供了抽象好的 CRUD 方法供开发人员使用,无需再编写 SQL 语句, Mybatis 的增强框架就借鉴了一部分 JPA 的思想。Spring Data JPA 进一步在 JPA 之上提供了更高层次的抽象和便利性,使得开发更加高效。
接入过程 官方文档指引:Accessing data with MySQL
环境说明:
JDK21Spring Boot 3.3.1Mybatis Plus 3.5.7
引入如下依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <dependencies > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > com.mysql</groupId > <artifactId > mysql-connector-j</artifactId > <scope > runtime</scope > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId > <scope > test</scope > </dependency > </dependencies >
在 application.yml 中添加数据库配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 server: port: 8811 spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/im?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver username: root password: 123456 jpa: show-sql: true
创建数据库表对应的实体类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 package com.sxh.entity;import jakarta.persistence.Entity;import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;import jakarta.persistence.Id;import lombok.Data;import java.time.LocalDateTime;@Entity @Data public class User @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.UUID) private String userUid; private String account; private String password; private String userName; private String userAvatar; private Integer sex; private String mobile; private LocalDateTime updateDate; private LocalDateTime createDate; private Integer isDelete; private Integer version; }
创建 mapper 文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public interface UserMapper extends JpaRepository <User , String > }
在 Spring Data JPA 官方文档中,这里继承的是 CrudRepository 类,而实际开发中推荐继承 JpaRepository,因为 JpaRepository 继承自 CrudRepository,这意味着它包含了 CrudRepository 的所有方法:
CrudRepository:提供了最基本的 CRUD 操作方法,适合不需要复杂数据库操作的应用场景。JpaRepository:在 CrudRepository 基础上扩展了更多功能,包括分页、排序和批量操作,适合需要更多 JPA 特性支持的应用场景。
之后我们编写一个测试类测试一下:
1 2 3 4 public void queryTest () printQueryResult("查询全部数据" , userMapper.findAll()); printQueryResult("自定义查询" , userMapper.findByUserName("张三" )); }
在 Spring Data JPA 的官方 API 文档中,提供了更多相关特性的介绍,建议阅读一下,地址见:Spring Data JPA
查询 在阅读下面的内容前,关于 jpql 和原生 sql 的区别需要先理解下。
jpql:查询的是实体对象及其关系,而不是直接查询数据库表。
1 2 select A from User A where A.userName = ?1
原生 SQL:直接查询数据库表和列。
1 2 select * from user where user_name = ?1
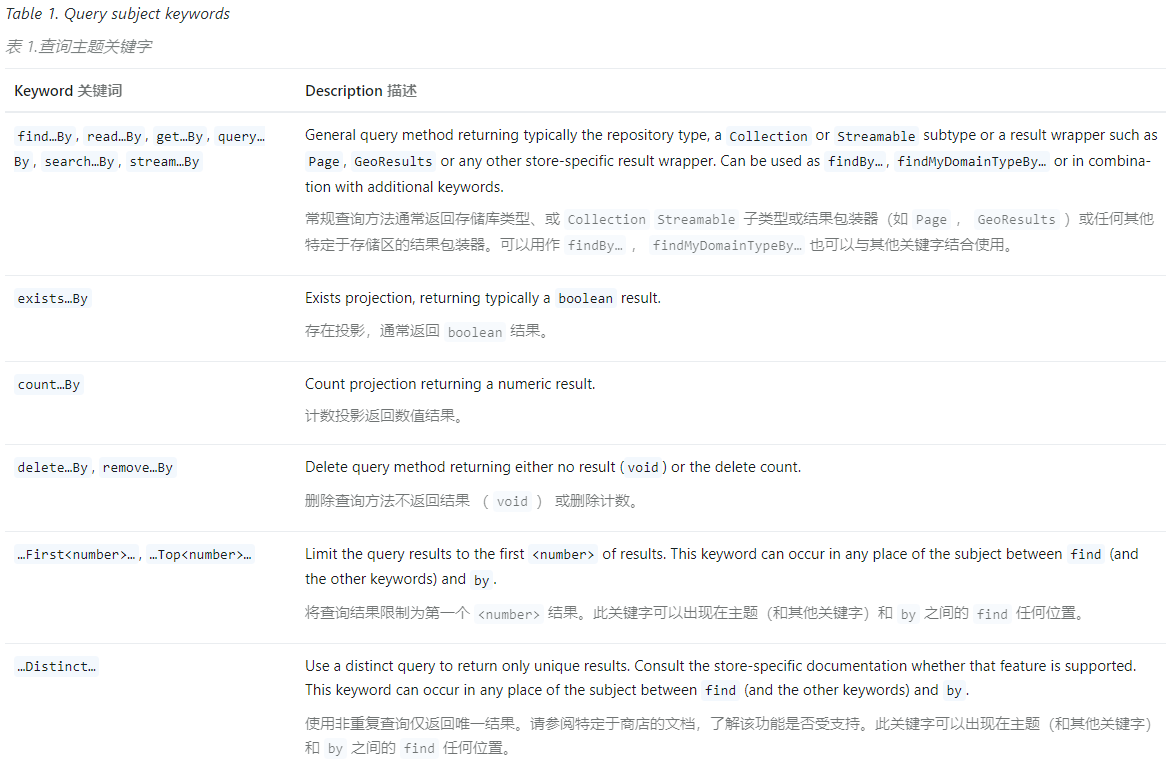
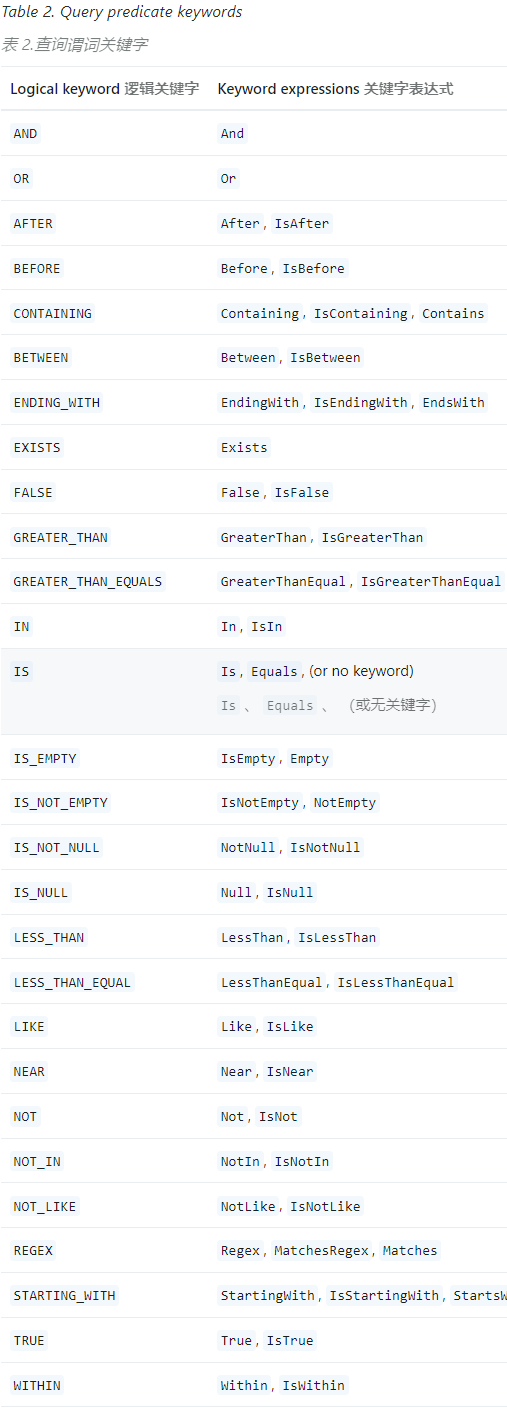
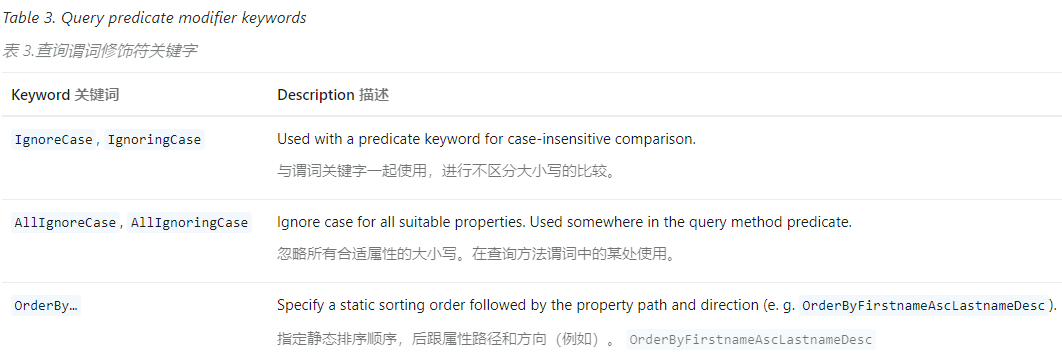
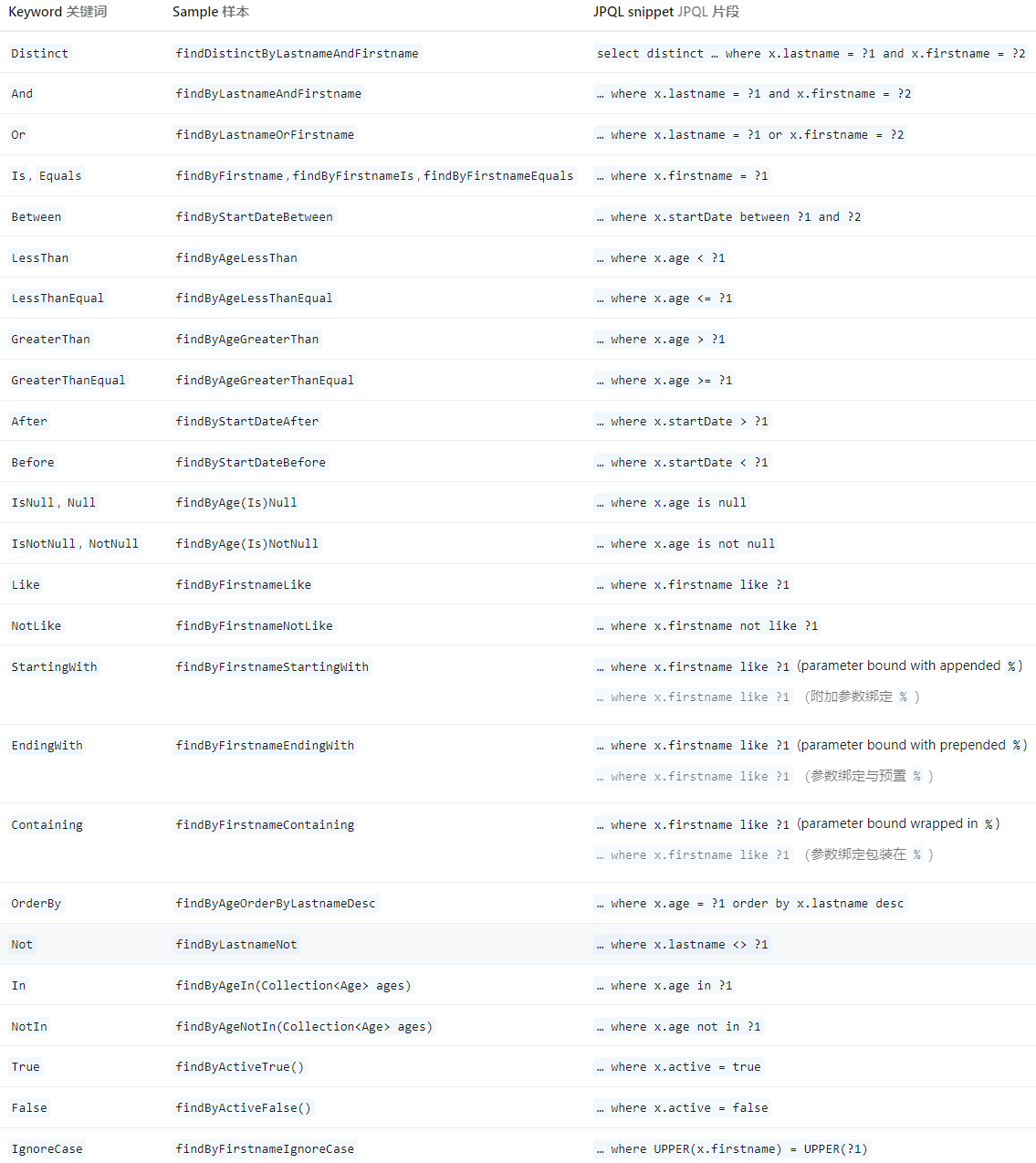
自定义查询 - 使用关键词 Spring Data JPA 提供了一套查询方法命名规则,使得我们可以通过命名来构建复杂的查询,Spring Data JPA 会基于方法名称的解析来自动生成查询语句。
Spring Data JPA 保留了一些关键词,用于解析我们自定义的查询方法,见:Repository query keywords 。关键词类型共有3种,如下
通过这套命名规则,我们可以自定义复杂的查询语句,具体可以见官方文档:JPA Query Methods 。下面的表格展示了包含特定关键词的方法的映射规则:
自定义查询 - 使用 EntityManger EntityManager 是 JPA(Java Persistence API)的核心接口之一,提供了对持久化上下文(Persistence Context)进行操作的方法。在 Spring Data JPA 中,EntityManager 被用来与数据库进行交互,执行 CRUD 操作、查询和事务管理。
在 EntityManager 中,我们可以构建下面几种查询:
entityManager.createQuery(jpqlQuery) - 创建基于 jpql 语句的查询。entityManager.createNativeQuery(sqlQuery) - 创建基于原生 sql 语句的查询entityManager.createNamedQuery(queryName) - 创建基于 @NamedQuery、@NamedNativeQuery 定义的语句的命名查询
当然 EntityManager 中还能创建其他查询,比如 entityManager.createStoredProcedureQuery - 构建基于存储过程的查询,日常开发使用频率较低,这里就不深入了。
下面测试下上面提到的三种查询。
使用 entityManager.createNamedQuery(queryName) 前,需要先在实体类中定义 @NamedQuery,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Entity @Data @NamedQuery(name = "customNamedQuery", query = "select A from User A where userName not like concat('%', ?1, '%')") @NamedNativeQuery(name = "customNamedNativeQuery", query = "select * from user where user_name not like concat('%', ?1, '%')", resultClass = User.class) public class User }
完整的测试类如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 @SpringBootTest public class SampleTest @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @PersistenceContext private EntityManager entityManager; @Test public void commonQueryTest () TypedQuery<User> query = entityManager.createQuery("select A from User A where A.userName not like concat('%', ?1, '%')" , User.class); query.setParameter(1 , "张" ); printQueryResult("使用EntityManger-createQuery构建查询" , query.getResultList()); Query nativeQuery = entityManager.createNativeQuery("select * from user where user_name not like concat('%', ?1, '%')" , User.class); nativeQuery.setParameter(1 , "张" ); printQueryResult("使用EntityManger-createNativeQuery构建查询" , nativeQuery.getResultList()); TypedQuery<User> customNamedQuery = entityManager.createNamedQuery("customNamedQuery" , User.class); customNamedQuery.setParameter(1 , "张" ); printQueryResult("使用EntityManger-createQuery构建@NamedQuery查询" , customNamedQuery.getResultList()); TypedQuery<User> customNamedNativeQuery = entityManager.createNamedQuery("customNamedNativeQuery" , User.class); customNamedNativeQuery.setParameter(1 , "张" ); printQueryResult("使用EntityManger-createQuery构建@NamedNativeQuery查询" , customNamedNativeQuery.getResultList()); } private void printQueryResult (String actionName, Object result) System.out.println("============================================" + actionName + "============================================" ); if (result instanceof List<?> list) { list.forEach(System.out::println); } else if (result instanceof Page<?> page) { System.out.printf("数据总数:%d,当前页:%d,总页数:%d,当前页数据:%d \n" , page.getTotalElements(), page.getNumber() + 1 , page.getTotalPages(), page.getNumberOfElements()); page.forEach(System.out::println); } else { System.out.println(result); } } }
自定义查询 - 使用 @Query 可以通过 @Query 自定义查询语句,在 @Query 中有一个 nativeQuery 参数:
值为 true 时,使用的是原生 sql 语句进行的查询
值为 false 时,使用的是 jpql 语句进行的查询
如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public interface UserMapper extends JpaRepository <User , String > @Query(value = "select * from user where is_delete = 1", nativeQuery = true) List<User> selectDeletedUserWithNativeQuery () ; @Query("select A from User A where A.isDelete = 1") List<User> selectDeletedUserWithoutNativeQuery () ; }
之后在测试类中调用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @SpringBootTest public class SampleTest @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test public void commonQueryTest () printQueryResult("@Query定义的查询语句-jpql" , userMapper.selectDeletedUserWithoutNativeQuery()); printQueryResult("@Query定义的查询语句-原生sql" , userMapper.selectDeletedUserWithNativeQuery()); } private void printQueryResult (String actionName, Object result) System.out.println("============================================" + actionName + "============================================" ); if (result instanceof List<?> list) { list.forEach(System.out::println); } else if (result instanceof Page<?> page) { System.out.printf("数据总数:%d,当前页:%d,总页数:%d,当前页数据:%d \n" , page.getTotalElements(), page.getNumber() + 1 , page.getTotalPages(), page.getNumberOfElements()); page.forEach(System.out::println); } else { System.out.println(result); } } }
自定义查询 - Specification 在 Spring Data JPA 中,Specification 是用于构建动态查询条件的一个功能强大的工具。它可以帮助你根据各种条件动态生成 SQL 查询,并支持复杂的查询条件组合。官方文档见:Specifications
实际使用中,我们的 Mapper 只需要继承 JpaSpecificationExecutor 类,就可以拥有通过 Specification 进行查询的能力。
1 public interface UserMapper extends JpaRepository <User , String >, JpaSpecificationExecutor <User >
看下 JpaSpecificationExecutor.java:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public interface JpaSpecificationExecutor <T > Optional<T> findOne (Specification<T> spec) ; List<T> findAll (Specification<T> spec) ; Page<T> findAll (Specification<T> spec, Pageable pageable) ; List<T> findAll (Specification<T> spec, Sort sort) ; long count (Specification<T> spec) boolean exists (Specification<T> spec) long delete (Specification<T> spec) <S extends T, R> R findBy (Specification<T> spec, Function<FluentQuery.FetchableFluentQuery<S>, R> queryFunction) ; }
写个测试类测试下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @SpringBootTest public class SampleTest @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Test public void commonQueryTest () Specification<User> specification = (root, query, cb) -> cb.notLike(root.get("userName" ).as(String.class),"%张%" ); printQueryResult("使用Specification查询" , userMapper.findAll(specification)); } private void printQueryResult (String actionName, Object result) System.out.println("============================================" + actionName + "============================================" ); if (result instanceof List<?> list) { list.forEach(System.out::println); } else if (result instanceof Page<?> page) { System.out.printf("数据总数:%d,当前页:%d,总页数:%d,当前页数据:%d \n" , page.getTotalElements(), page.getNumber() + 1 , page.getTotalPages(), page.getNumberOfElements()); page.forEach(System.out::println); } else { System.out.println(result); } } }
构建分页查询的几种方式 上面提到,实际开发中建议继承 JpaRepository 完成 CRUD 操作,除了 CRUD 操作外,JpaRepository 还提供了分页、排序、批量处理的操作,其中分页功能是通过继承了 PagingAndSortingRepository 类实现的,我们看下这个类:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public interface PagingAndSortingRepository <T , ID > extends Repository <T , ID > Iterable<T> findAll (Sort sort) ; Page<T> findAll (Pageable pageable) ; }
这个类提供了一个简单的分页操作,我们从返回值 Page 可以拿到如下几个属性: 总数据量、当前页、总页数、当前页数据量。
实际开发中,分页查询还需要提供各种查询条件,我们可以通过上面提到的几种自定义查询方法来构建分页查询。
通过 @Query 来构建分页查询,需要在 Mapper 中事先定义好对应的语句;通过 Specification 构建分页查询,则需要 Mapper 继承 JpaSpecificationExecutor 类,Mapper 文件如下,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public interface UserMapper extends JpaRepository <User , String >, JpaSpecificationExecutor <User > Page<User> findByUserNameNotLike (String userName, Pageable pageable) ; @Query(value = "select * from user where user_name not like concat('%', ?1, '%')", countQuery = "select count(1) from user where user_name not like concat('%', ?1, '%')", nativeQuery = true) Page<User> selectByUserNameNotLikeWithNativeQuery (String userName, Pageable pageable) ; @Query(value = "select A from User A where A.userName not like concat('%', ?1, '%')", countQuery = "select count(1) from User A where A.userName not like concat('%', ?1, '%')") Page<User> selectByUserNameNotLikeWithoutNativeQuery (String userName, Pageable pageable) ; }
完整测试类如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 @SpringBootTest public class SampleTest @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @PersistenceContext private EntityManager entityManager; @Test public void pageQueryTest () printQueryResult("分页查询" , userMapper.findAll(PageRequest.of(0 , 5 ))); Sort sort1 = Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "createDate" ); printQueryResult("排序查询" , userMapper.findAll(sort1)); Sort sort2 = Sort.by("createDate" ).descending().and(Sort.by("updateDate" ).ascending()); printQueryResult("排序并分页" , userMapper.findAll(PageRequest.of(0 , 5 , sort2))); printQueryResult("自定义分页查询" , userMapper.findByUserNameNotLike("%张%" , PageRequest.of(0 , 5 , Sort.by("createDate" ).descending()))); Specification<User> specification = (root, query, cb) -> cb.notLike(root.get("userName" ).as(String.class),"%张%" ); printQueryResult("使用Specification进行分页条件查询" , userMapper.findAll(specification, PageRequest.of(0 , 5 , Sort.by("createDate" ).descending()))); printQueryResult("通过EntityManager-nativeQuery构建分页查询" , pageQueryByEntityManager(PageRequest.of(0 , 5 ))); printQueryResult("通过@Query-nativeQuery构建分页查询" , userMapper.selectByUserNameNotLikeWithNativeQuery("张" , PageRequest.of(0 , 5 ))); } private Page<User> pageQueryByEntityManager (PageRequest pageRequest) String sqlStr = "select * from user where user_name not like concat('%', ?1, '%')" ; Query nativeQuery = entityManager.createNativeQuery(sqlStr, User.class); nativeQuery.setParameter(1 , "张" ); nativeQuery.setFirstResult((int ) pageRequest.getOffset()); nativeQuery.setMaxResults(pageRequest.getPageSize()); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List<User> users = nativeQuery.getResultList(); Query countQuery = entityManager.createNativeQuery("select count(1) from user where user_name not like '%张%'" ); long total = ((Number) countQuery.getSingleResult()).longValue(); return new PageImpl<>(users, pageRequest, total); } private void printQueryResult (String actionName, Object result) System.out.println("============================================" + actionName + "============================================" ); if (result instanceof List<?> list) { list.forEach(System.out::println); } else if (result instanceof Page<?> page) { System.out.printf("数据总数:%d,当前页:%d,总页数:%d,当前页数据:%d \n" , page.getTotalElements(), page.getNumber() + 1 , page.getTotalPages(), page.getNumberOfElements()); page.forEach(System.out::println); } else { System.out.println(result); } } }
参考文档 Accessing Data with JPA - 官方接入文档
Spring Data JPA使用:看这一篇就够了
@Autowired vs @PersistenceContext for EntityManager bean
【一目了然】Spring Data JPA使用Specification动态构建多表查询、复杂查询及排序示例
[Spring Data JPA - 官方Api文档